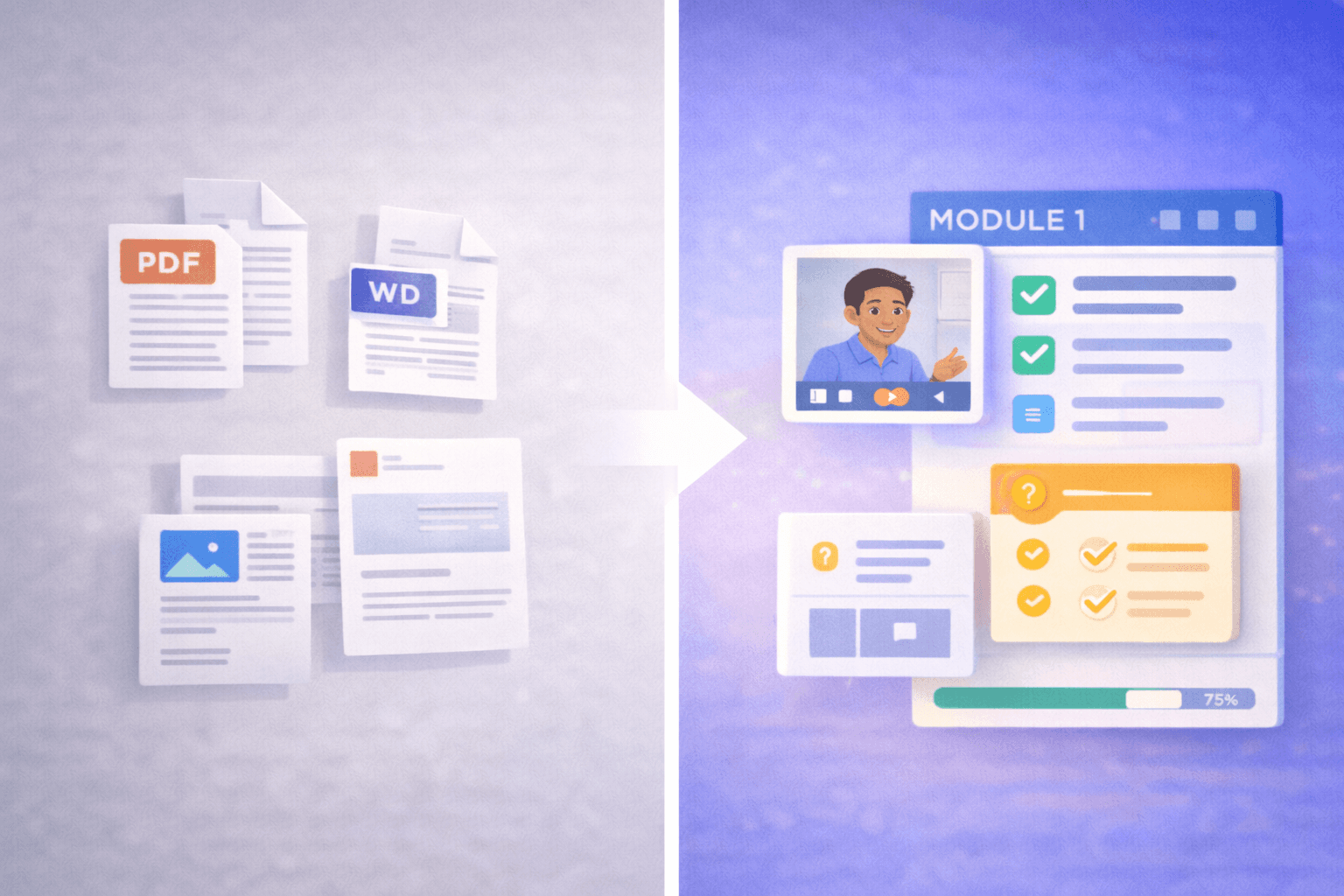
Curating knowledge
12 examples of professional training programs in the workplace
This article walks through practical examples of professional training used across modern workplaces. It also shows how teams move faster by turning existing content into structured training instead of starting from scratch.

Ryan Macpherson
Feb 12, 2026

Editor:
Stephanie Chan
According to a LinkedIn Learning report, 94% of employees say they would stay at a company longer if it invested in their learning and development. But training still feels slow, scattered, and hard to scale.
Most companies already have the raw material for strong employee training programs. It lives in onboarding docs, SOPs, slide decks, and shared folders. Useful knowledge stays trapped. Training initiatives stall. New hires piece things together on their own.
That gap creates real costs. Slower ramp time. Uneven skills training. Frustrated employees who never quite feel equipped for their job positions.
This article walks through practical examples of professional training used across modern workplaces. It also shows how teams move faster by turning existing content into structured training instead of starting from scratch.
Inside, you’ll find:
The most common professional training programs teams rely on
What each training supports at different stages of employee development
Why training content often slows down or gets stuck
A more practical way to create and update training as teams grow
What is professional training?
Professional training is structured learning that helps employees perform better in their roles and build toward what’s next.
In practice, it includes training programs tied to real work tasks:
Onboarding for new employees
Compliance training
Skills training that supports day-to-day work
Effective professional development focuses on application. Employees learn specific skills, use them in their current position, and build confidence over time. That supports career development, job satisfaction, and employee retention.
12 examples of professional training in the workplace
Professional training takes many forms across an organization. Some programs focus on compliance or safety. Others support skill-building, career growth, or improved collaboration.
Below are the types of workplace training teams rely on most, along with why they matter and how they’re typically used.
1. Onboarding and orientation training
Onboarding and orientation training help new hires understand how the company works and what’s expected of them.
Orientation training usually covers the basics, such as policies, tools, and company culture. It often happens during the first few days.
Onboarding goes further. It’s a structured employee training program that can run for a few weeks. New employees learn role-specific tasks, workflows, and necessary skills to succeed in their new job.
Strong onboarding reduces ramp time, improves employee engagement, and helps employees feel supported early on.
2. Compliance training
Compliance training covers the rules and regulations employees must follow to keep the business safe and legally protected.
This type of employee training often includes topics like:
Workplace conduct: Covers expectations for professional behavior, helping employees understand boundaries, responsibilities, and acceptable interactions at work.
Data privacy: Trains employees on how to handle sensitive information responsibly and comply with data protection standards.
Cybersecurity: Focuses on recognizing threats and following safe practices to protect company systems and information.
Health and safety requirements: Outlines procedures and precautions that help prevent accidents and maintain a safe work environment.
In regulated industries, it may also cover role-specific obligations tied to job positions.
Compliance training protects the organization. It also protects employees. Clear expectations reduce risk, confusion, and avoidable mistakes.
3. Technical skills training
Technical skills training focuses on the hard skills employees need to do their work effectively.
This includes software proficiency, system training, and role-specific tools. For some teams, that means software development or data analysis. For others, it may involve internal systems, reporting tools, or industry platforms.
Technical skills training helps employees close skills gaps and keep pace as tools change. It also supports current employees who need to build new skills as their responsibilities evolve.
Well-designed technical skills training equips employees to work independently, reduces errors, and supports long-term employee development.
4. Product and service training
Product and service training helps employees understand what the company offers and how it works.
This training is essential for sales, support, and customer-facing teams. Employees learn features, use cases, pricing basics, and common customer questions. For support teams, it also covers troubleshooting and escalation paths.
Strong product training leads to better conversations. Employees understand the value behind what they’re selling or supporting. Customers get clearer answers. Issues resolve faster.
Structured product training turns that knowledge into a shared reference. Training stays current as products change, and employees always know where to look when questions come up.
5. Sales training
Sales training focuses on the skills employees need to move deals forward with confidence.
It often includes prospecting techniques, objection handling, pipeline management, and CRM usage. Sales teams also train on messaging, qualification frameworks, and how to position products in different scenarios.
Strong sales training shortens ramp time for new hires and sharpens performance for current employees. Reps follow consistent processes. Managers spend less time correcting basics and more time coaching.
Structured sales training programs turn content into repeatable learning. Reps can revisit techniques, reinforce skills after training sessions, and build confidence over time.
This sales training course was created using Coassemble, a knowledge transfer platform that turns existing documents and decks into structured, trackable training. Teams can add quizzes and AI narration, then share courses by link or connect them to an existing LMS.

6. Leadership and management training
Leadership and management training focuses on building leadership skills at every level of the organization.
It supports new managers stepping into their first people role, experienced leaders managing larger teams, and senior leaders shaping strategy. Common topics include delegation, feedback, decision-making, and performance management.
Strong leadership training improves team clarity and trust. Managers communicate expectations clearly. Employees feel supported. Teams stay aligned with business goals.
Leadership content often starts as workshops or in-person training. Slides get shared. Notes get taken. Then the knowledge fades.
Leadership training works best when it’s ongoing. Clear lessons. Practical examples. Content that grows with the team.
7. Soft skills training
Soft skills training focuses on how employees communicate, collaborate, and resolve issues at work.
It covers communication training, conflict resolution, emotional intelligence, and time management. These skills shape team dynamics and influence job satisfaction more than most technical skills.
With Coassemble, teams can turn workshop materials and facilitator notes into structured training courses that stay available as teams grow. Communication expectations stay consistent. New hires learn faster. Managers reinforce the same standards across teams.
8. Diversity and inclusion training

Diversity and inclusion training helps employees understand how to work respectfully across different backgrounds, roles, and perspectives.
It often covers topics like unconscious bias, inclusive communication, and workplace behavior. The goal is a safer, more respectful work environment where employees feel supported.
Many teams treat this training as a once-a-year requirement.
Teams can turn DEI materials into ongoing training programs that evolve with company culture. Content stays clear, consistent, and accessible to both new hires and current employees.
9. Safety training
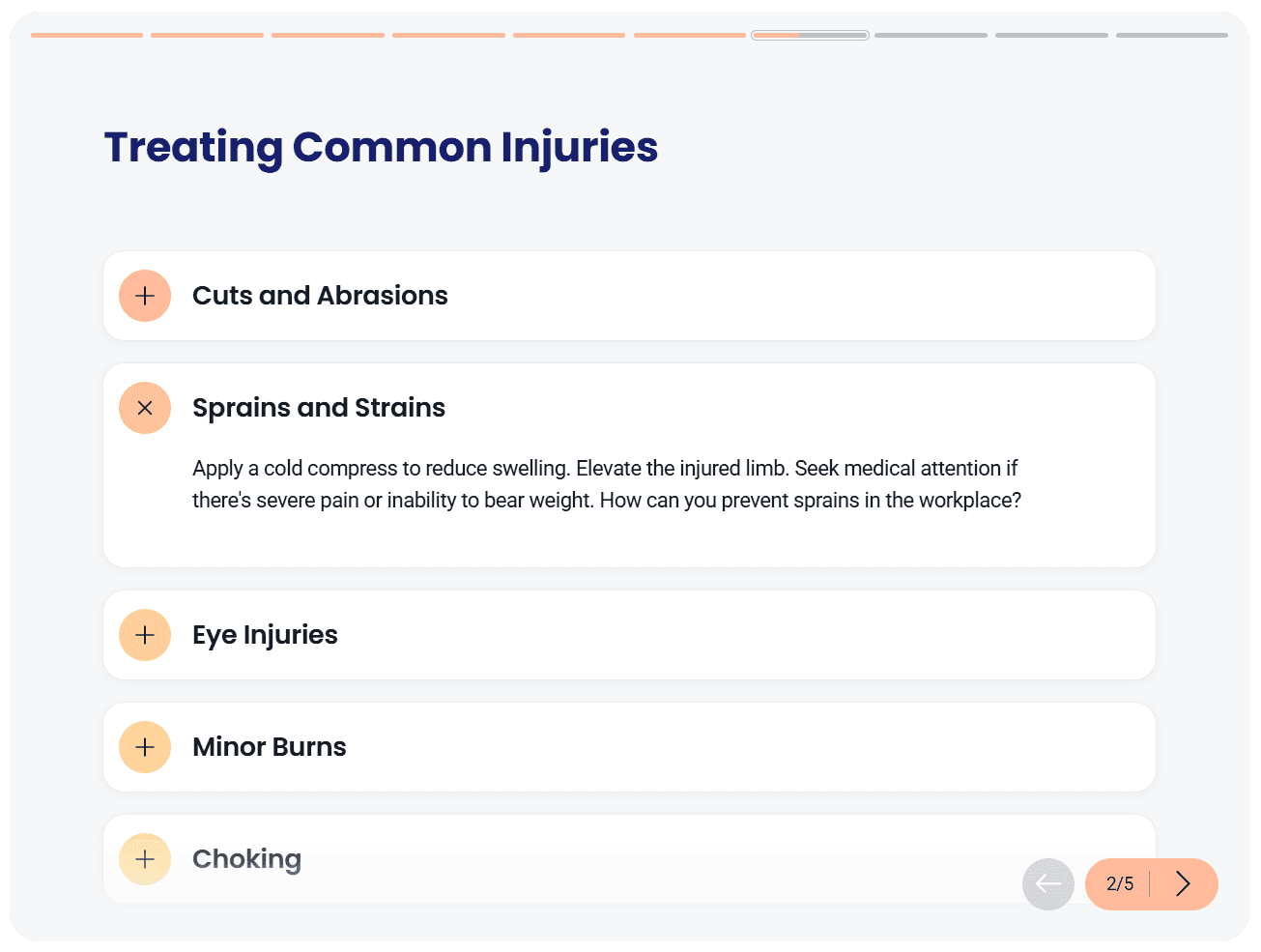
Safety training focuses on protecting employees during everyday work.
It includes physical safety protocols, emergency procedures, and proper equipment use. In some roles, it also covers job-specific risks tied to work tasks or environments. A clear safety training program reduces accidents and supports regulatory compliance.
When safety information is structured into a safety training program, employees understand expectations before issues arise.
Safety training works best when it’s direct, easy to access, and kept current without friction.
10. Quality assurance training
Quality assurance training helps employees understand standards, processes, and quality checks tied to their work.
It’s common in operations, support, and production roles. Employees learn how to meet expectations, spot errors, and maintain consistency across outputs. Strong quality assurance training reduces rework and improves customer trust.
When quality assurance training is structured into clear training programs, employees understand what “good” looks like. Teams follow the same standards. Issues are easier to catch early.
Quality assurance training supports consistency without slowing teams down.
11. Customer service training
Customer service training equips employees to handle customer interactions with confidence and clarity.
It covers product knowledge, communication skills, de-escalation techniques, and issue resolution. For many roles, this training directly shapes customer experience and brand perception.
Customer service knowledge often sits across scripts, help docs, and internal notes. Employees learn by shadowing co-workers or asking questions in the moment.
Strong customer service training helps employees respond calmly, resolve issues faster, and deliver a more consistent experience.
12. Upskilling and reskilling programs
Upskilling and reskilling programs help employees build new skills as roles and business needs change.
Upskilling focuses on expanding existing skills. Reskilling prepares employees for new job positions or responsibilities. Both support career development and long-term employee retention.
Teams can organize learning paths into clear development programs tied to business goals. Employees understand what to learn next and why it matters. Progress stays visible without heavy administration.
Upskilling and reskilling work best when learning is practical, accessible, and aligned with real career growth.
How to create professional training with Coassemble
The examples above all have one thing in common. Most teams already have the knowledge to run these training programs.
Onboarding guides exist. Compliance policies are written. Sales playbooks and leadership frameworks live in shared folders. The challenge is turning that material into professional training employees can actually use.
Coassemble removes that bottleneck by helping teams transform everyday documents into structured, trackable training without long timelines or specialized roles.
Here’s what that process looks like.
Step 1: Open the course builder

Start by opening Coassemble's course builder and selecting Start creating. The course builder loads instantly, so you can explore how it works before setting anything up.
Step 2: Start from existing content

When the builder opens, choose how you want to create your training. For most employee training programs, the fastest path is transforming content you already have.
Upload a PDF, PowerPoint, or Word document. Coassemble’s AI scans the file, identifies key ideas, and organizes them into a structured training course.
Step 3: Set the direction
After uploading your content, you’ll answer a few short questions. These shape the course before it’s generated.
You’ll be asked things like:
What should your audience achieve from this course?
How would you describe your audience?
These inputs help the AI align tone, structure, and learning objectives with your audience.
Step 4: Review the generated course

Once the setup is complete, Coassemble generates a full draft in seconds. Lessons appear in sequence with the structure already in place.
You can click through each section to check flow, accuracy, and clarity.
When you’re ready, click Continue.
Step 5: Share training where work happens
Before publishing, you’ll see optional enhancements like quizzes or branding. Add them if needed, or move ahead.
Then choose how to deliver the training:
Share a link in Slack, Teams, or your intranet
Send email invitations
Export a SCORM file to your LMS or HRIS
Embed training directly into your platform (Enterprise)
Pick a method then click Proceed.
Step 6: Save, track, and improve
To save and share your course, create a free Coassemble account. This keeps your training editable and accessible.
Learners can open courses without extra logins. Teams get a clear view of completions and quiz results, with deeper learner insights available on paid plans.
That visibility makes it easier to see what’s working and where support is needed.
Professional training doesn’t need to start from zero.
With Coassemble, existing knowledge moves faster, stays current, and reaches the people who need it when they need it.
Wrapping up
Professional training covers a wide range of needs. Each program supports employees at different stages of their work and career growth.
The hard part isn’t identifying the right training programs. It’s delivering them in a way that’s timely, consistent, and easy to maintain.
Most organizations already have the content. It just isn’t structured for learning.
When knowledge moves out of static documents and into clear training courses, professional development becomes easier to sustain. Training stays current. Employees feel equipped. Teams stay aligned as business goals change.
Coassemble closes the gap between knowing what training is needed and actually delivering it. It helps teams turn existing knowledge into professional training that’s clear, trackable, and ready to share without long build cycles or heavy resources.
FAQs about professional training
What is a professional training program?
A professional training program is a structured approach to developing employee skills, knowledge, and performance. It focuses on practical learning tied to real job responsibilities and business goals.
What is an example of professional learning?
An example of professional learning could be onboarding training for new hires, leadership development for managers, or technical skills training that helps employees use tools more effectively.
What are 5 professional skills examples?
Common professional skills include communication skills, leadership skills, conflict resolution, time management, and problem-solving. These skills support performance across many job positions.
What are the 4 types of training?
Four common types of training include onboarding and orientation training, technical skills training, compliance training, and leadership or professional development programs.
Read More
Join the knowledge revolution today
Unlock knowledge. Boost engagement. Drive results
No credit card required

Join the knowledge revolution today
Unlock knowledge. Boost engagement. Drive results
No credit card required

Join the knowledge revolution today
Unlock knowledge. Boost engagement. Drive results
No credit card required